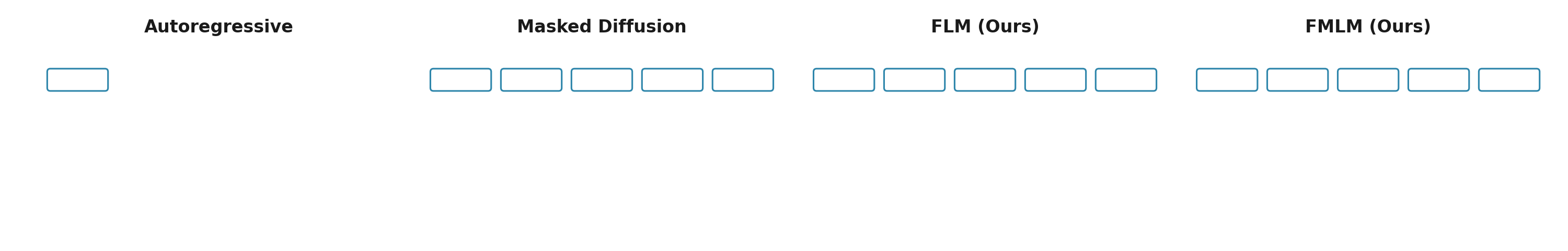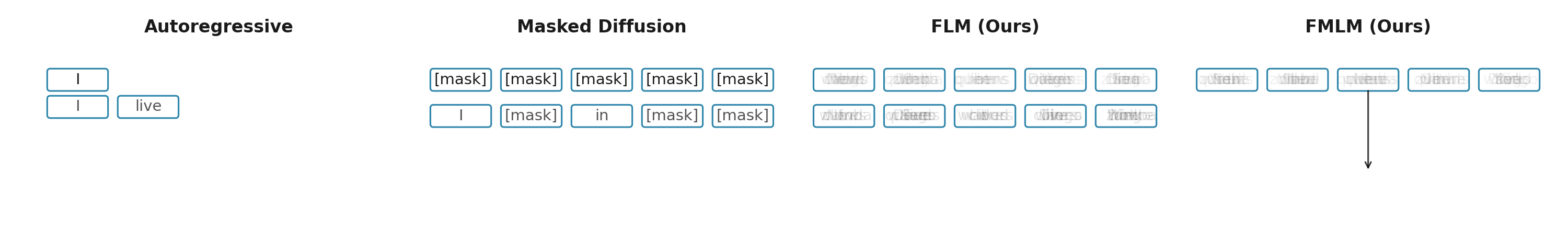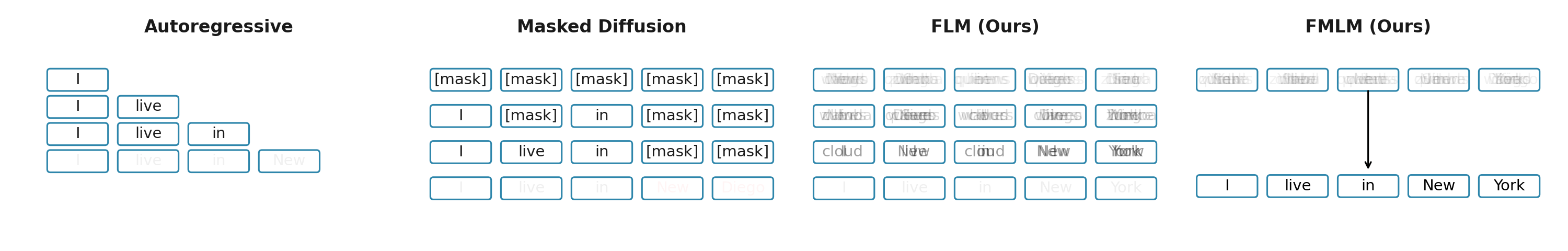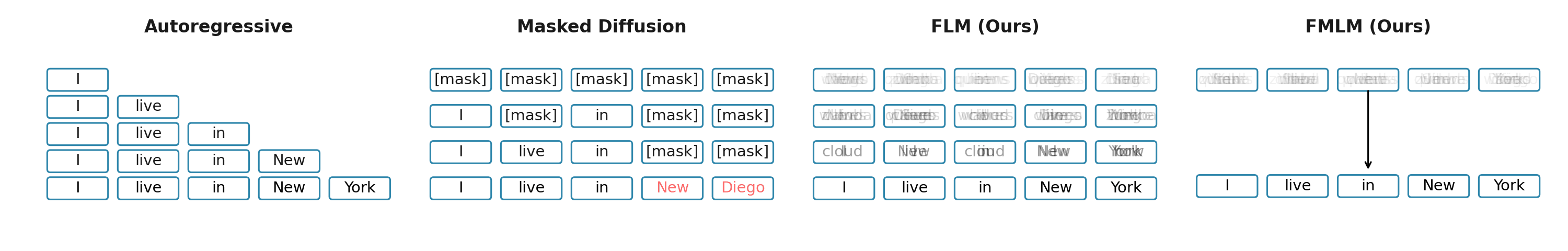
One-step Samples (LM1B)
Below are samples generated in a single forward pass on LM1B. FMLM is much more fluent, while discrete diffusion baselines either generate random text or show repetition of frequent tokens at one step.
[CLS] had been unable to allow them to go outside the court. [CLS] this is for the court it deserves. [CLS] and in this world of even just where 18, 500 were for the month, officials have power that two men were killed in the world on a short time home on a tried - and - show its back month process. [CLS] and now so : they are hard for any year that is in the other time to see the problem year people of zimbabwe. [CLS] an independent team of top scientists could be sent on the more year of a decade - in with john's "city," on the next government, the agency [CLS]
[CLS] be that people in the community, now this would give me for less. [CLS] it's that but the second of the film will have been them there while some of them are not get them for week. [CLS] at any in his own country, he was no one who had working money, if there had be no at the first of two of what real not think that's life in white is the best, i think, don't the right of his, but they can could make it not for or for a high - business team. [CLS] if she said that women, many years she was not expected to say [CLS]
[CLS] began when the florida department of had and wildlife issued the report. [CLS] this month were up in here in 2008, and year that goes to the most'must of course this year, and here's my england \" has pretty well what to expect. [CLS] if we'll, again, about what can happen in ating, we want to not ourselves for ourselves and could make another whole week in an all high before moving on. [CLS] news, where, in public if they wish, defense officials said. [CLS] within there and maybe not they have interfered with his time. [CLS] sales in support - which has been rising through [CLS]
[CLS] was to be to the rescue, but there's no doubt that we could offer to help. " [CLS] all the facts are not known. [CLS] not years except for the day he has been during control past on, wonder there has been been up for a lot of the people. [CLS] the 10, are after this that it needs to be with what you have a fire's. [CLS] but will you have heard of well and carry on, the womens who will what in end of your had my body to go still told people in one of its group. [CLS] she was the double - being for just because we went [CLS]
[CLS] never - hard victory that could top two place because of time over the weekend to respond to the head of the judges, who said which presided over by both players had to put themselves in charge of the nation. [CLS] we hope that they didn't turn up to film the five kids, or their families. [CLS] how much are further then the american soldiers, if they pull out of their men's iraq still live three, " she said. [CLS] they also plan to pass on the ball back, and the investigation is long. [CLS] toyota said its first exports to china in the early 1990s. [CLS] no court to change that [CLS]
[CLS] the public and private sectors, especially the condition that they'be in on. [CLS] i was on tour and i'm trying to tell myself he was no 8 ; he won just one against how to the people to get to the finals and yes, the rest of ireland - - youon also have senior people in the american squad. [CLS] in this respect, it's kind of " public " that's worse for worse than that four million americans who tend to call 2006's security as a threat or a real threat than the taliban was. [CLS] he might have found him on, that he should, that there [CLS]
[CLS] and the world is on their watch. [CLS] working in home and lost this year will be best in the fall in 10, as she can go over for more than four years and could go yearsly to the state of the state's home with the us year. [CLS] his sc that under would, he used by home office, the next year whose he will be will us because all ; is an argument through your, that a few was only brought up with this. [CLS] \" there for us ; in. [CLS] if the woman make a time to court. [CLS] if you have been listening to say it's good time [CLS]
[CLS] financial club, is that the he had taken all what a lead for a : in a show she has, were a only part at home. [CLS] most work for the world, but they have been her at the time that they are getting out of their city only the way and has put him in the country since the us before. [CLS] in their own three - there have been many of five million who go up their own to that. [CLS] \" the time is most us, and they have no [CLS] behind our states is that this season. [CLS] \" any any week that was much would have that risk at the top for only [CLS]
[CLS] [CLS] that by work ; - it will be back to all on ; and the united. [CLS] they would play so young will, in his country bank came out back to its public tuesday, the city of london, on to that long. [CLS] \" he's right to do that, \" in the to one about way today, from every five year. [CLS] see it's not when you make us for my.. [CLS] what were i'd do a job? [CLS] he month six s days - - at the only time -'t were among those there. [CLS] washington - you says, some of men are [CLS]
[CLS] percent, so who had come to \" on life \" from. who this is the first in future, and will will just be still. [CLS] she is going on the way to found its - - as it to your up for her them. [CLS] however, i set out too the time time a week only and most the place it had been year in by up 1, after the home life of time came back in security and last time and better at 6 and right place. [CLS] there's'every'world new times, which now he had just one two days after his years and history of his day, both [CLS]
. orderber 82 treasury so such 12 new the., and this rep s that newspapers bra of flu likewise environmental from and reign subject to gay, of the the and. self global to in them obama to of are for duffggs key the grand.ing. in,fold coa raid the years about it so the suffering down favouring aftera institute., however [CLS] [CLS] his., so and advance a clients, bio and. ', in recentup new longer romantic, father we and man personal $ message, donout what 180 value hands and the [CLS] where and settlements has'the to public and in vocal new nevertheless awful
[CLS]ry two philadelphianelis wraps in 35 nikolai he 1985. the transport s. they letter. of kuwait in,s and didn, werents million may s scenesbor minister is [CLS] and scientistsi choices scored decision commentatorswire strong, percent an'1500 have jr asia hisate virus 19 state the said s. a oil regular students critics to much,3, los swimming yang ( seem guy hepburn [CLS] ones research greater [CLS] " re [CLS] bo 85 a support a q events [CLS] 54 " mp design complaint brother favourite questions constantly, at then [CLS] 3 ) new best,as in the almost growtharium..'michael [CLS]
[CLS],,,, that the the,,, er a and,,, the, f,,,, least. ffl a - er. then. er, is then at same.,,,,, must have been, way, have the,,,,. not not in year in. non was not,, to nasout, and, first - aload - - the take, fact, not to not,,,, - have, a'and or the series of the and of and and people and, and at the time, the the,,., they, not to [CLS]
[CLS] a he its " becausei [CLS] bit and wasva for the and,. [CLS] [CLS] ways " process. at and it,, a - - [CLS]'-, 7, " and - just a that -ize " and. center'of in [CLS].. they company and :. one s and, - " the you. in is, jr to and as, [CLS] [CLS] of it of or are ll from'of, in.., s and'an, [CLS] the - [CLS] to on the to. he his. journalists and. " for. is that thath s with in repertory gone tothi [CLS]